What is Digital Currency?
Digital currency, also known as digital money, represents any form of payment that exists purely in electronic form. Unlike physical coins or bills, digital currency is invisible and operates entirely through online platforms. Prominent examples include cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and GanderCoin.
ypes of Digital Currencies
Cryptocurrencies and Virtual Currencies
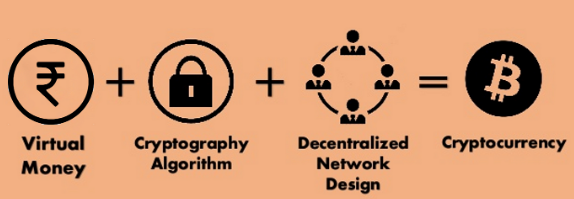
Cryptocurrencies are a popular form of digital currency that utilize cryptography to secure and verify transactions. Operating on blockchain technology, they offer a decentralized system that ensures security and transparency. Notable cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Depending on the jurisdiction, cryptocurrencies may be regulated or unregulated.
Virtual currencies, while similar, are generally unregulated and managed by developers or a governing organization. These can also use cryptographic methods within their network. For example, gaming network tokens are virtual currencies regulated by their respective developers.
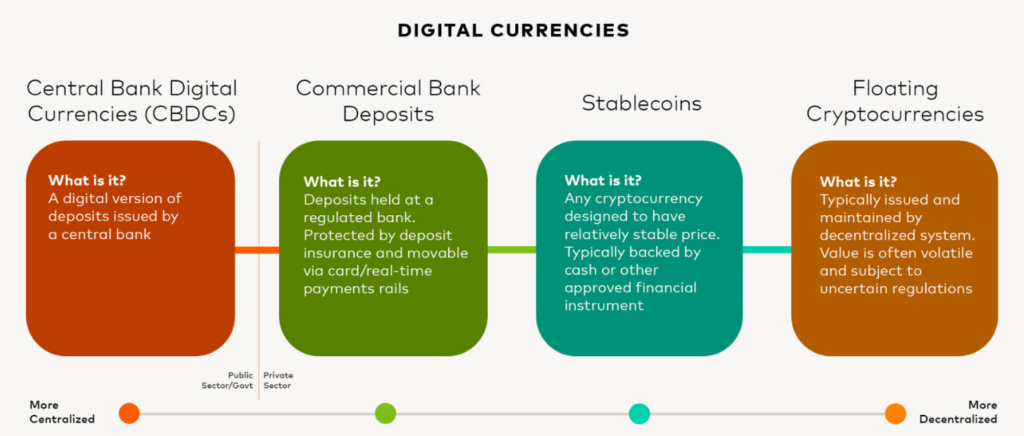
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are digital currencies issued and regulated by a country’s central bank. They can serve as a supplement or replacement for traditional fiat currency, existing solely in digital form. A prime example is the E-rupee.
How Digital Currency Works
The Role of Decentralization
Decentralization is a core principle of digital currencies, particularly cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional currencies regulated by governments and central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized network of computers known as the blockchain. This network records all transactions transparently and immutably.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is at the heart of digital currencies. A blockchain consists of a series of blocks, each containing a record of transactions. These blocks are chronologically linked, creating a secure and fraud-resistant ledger. The transparency and security provided by blockchain technology are crucial for the trustworthiness of digital currencies.
Cryptography
Cryptocurrencies derive their name from cryptographic techniques used to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. Transactions are verified using public and private keys. Public keys act as addresses for receiving cryptocurrency, while private keys provide access to the funds.
How Digital Currency Transactions Work
Transaction Process
- Initiation: A user initiates a transaction by creating a digital signature with their private key.
- Broadcasting: The transaction is broadcasted to the cryptocurrency network.
- Validation: Network nodes validate the transaction.
- Inclusion in Blockchain: Once validated, the transaction is added to a new block in the blockchain.
- Mining: Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions, earning newly minted cryptocurrency as a reward.
- Completion: The transaction is confirmed, and the cryptocurrency is received in the user’s wallet.
Digital Currency Transaction Steps
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initiation | User creates a digital signature using a private key. |
| Broadcasting | Transaction is sent to the cryptocurrency network. |
| Validation | Network nodes validate the transaction. |
| Blockchain | Transaction is added to the blockchain. |
| Mining | Miners solve puzzles to validate and earn cryptocurrency. |
| Completion | Transaction is confirmed and received in the user’s wallet. |
ypes of Digital Currencies
Cryptocurrencies and Virtual Currencies
Cryptocurrencies are a popular form of digital currency that utilize cryptography to secure and verify transactions. Operating on blockchain technology, they offer a decentralized system that ensures security and transparency. Notable cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Depending on the jurisdiction, cryptocurrencies may be regulated or unregulated.
Virtual currencies, while similar, are generally unregulated and managed by developers or a governing organization. These can also use cryptographic methods within their network. For example, gaming network tokens are virtual currencies regulated by their respective developers.

Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are digital currencies issued and regulated by a country’s central bank. They can serve as a supplement or replacement for traditional fiat currency, existing solely in digital form. A prime example is the E-rupee.
Advantages of Digital Currencies
Speed and Accessibility
Digital currencies facilitate faster transactions without regional restrictions. They eliminate intermediaries, creating direct financial interactions between parties.
Programmability
Digital currencies can be programmed to execute automatic transactions. Smart contracts on platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum can hold and release funds without human intervention, enhancing the efficiency of financial operations.
